Geo Firewall
Technical Specifications
| Latest release |
4.9 ,
5 Aug 2024 ,
[Change Log, Previous Releases]
|
| Supported networking |
Ethernet, IPv4, IPv6, TCP, UDP. |
|
Traffic filtering engine
|
Kernel-mode network driver. |
| Prerequisites |
.NET 4.5.2, up-to-date root certificates (or it will
take 2 minutes to start).
|
| Supported OSes |
Windows 7*, 8, 8.1, 10, 11, Server 2008 R2*, Server 2012, Server 2012 R2, Server 2016, Server 2019, Server 2022.
*For Windows 2008 R2 and 7, required Service Pack 1 +
KB3033929 (SHA-2 digital signing).
*For Windows 8.1, Server 2012 R2, required KB2995730.
|
| Recommended hardware |
CPU 1GHz and above, modern graphics card. |
| Additional hardware required |
none |
Overview
Very few people
realize that a large number of security threats comes from the
limited number of countries that ignore cyber threats until they reach dangerous proportions. In such countries,
web
servers are frequently compromised and infected with various
malware. As a consequence, those who visit them are running the risk of being infected with malware.
Quite often,
Internet users are totally unaware of the location of
servers just as they are unaware of where web links are taking them.
Geo Firewall shows which countries are being accessed. It
allows to block geographical regions, individual countries,
and custom networks.
Up until recently, the geographical (Geo-IP)
blocking was only available to large companies with
sophisticated and expensive hardware firewalls. Now, Geo Firewall brings such security to laptops, desktops, and
cloud servers. Once
geographical blocking rules are set, the computer is protected from reaching the blocked territories.
Geo Firewall is a security software that allows to separate the countries you trust from those
that you don't. It is compatible with most other security software. The more levels of defense there is, the
harder it is to breach.
Geo Firewall
IMPORTANT: When used on a Virtual Machine, accidental changes by a user to the rules may affect Remote Desktop (RDP) traffic and result in a user lock out.
For instructions on how to restore RDP connectivity for a VM, see KB article Restoring Remote Desktop (RDP) connectivity to Azure VM after a user lock out.
The operation of Geo Firewall is
straightforward. The tree-like list contains geographical
territories that are used for creating rules: checked (blocked)
or unchecked (allowed). The toolbar and the menu contain
operations that can be performed on the territories. The rules
work on IPv4/IPv6, TCP, and UDP network protocols.
Geo Rules
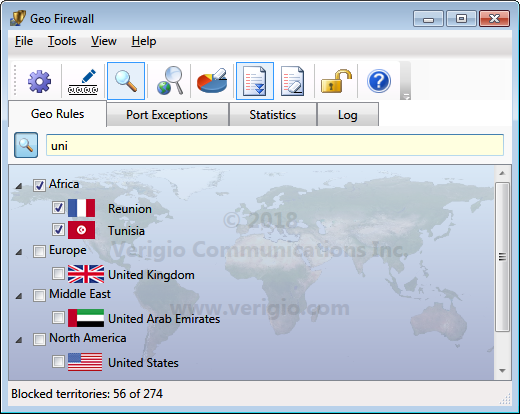
A checkmark on a geographical territory designates it as blocked. The search for individual countries by their name among
250+ available territories could be a daunting task.
The text search bar helps to make it easy by showing only the countries containing a certain text in their name.
Click
 button on the toolbar and only the countries containing specified text will stay visible.
button on the toolbar and only the countries containing specified text will stay visible.
Rules are automatically applied after every change with a default delay of 1 second. The delay can be changed within Settings
to allow more changes to be performed before the wait cursor comes up.
The program acts as a Windows service. So the rules are in effect while the "Geo Firewall" service is running. The
last rules are automatically loaded upon "Geo Firewall" service start.
To protect rules from accidental changes, read-only mode can be activated with
 button.
button.
Port Exceptions
Geo Firewall rules allow to block or to allow whole countries and networks. When used on servers, there are cases when computers
from the blocked countries need to have access to only a certain range of TCP or UDP ports.
In such cases, Port Exceptions allow to specify exclusions from the blocking rules. Each Port Exception
can have multiple port ranges that allow network traffic to local TCP/UDP ports.
Each Port Exception can also be bound to (associated with) multiple geographical territories, but a geographical
territory can be bound
only to (associated with) a single Port Exception.
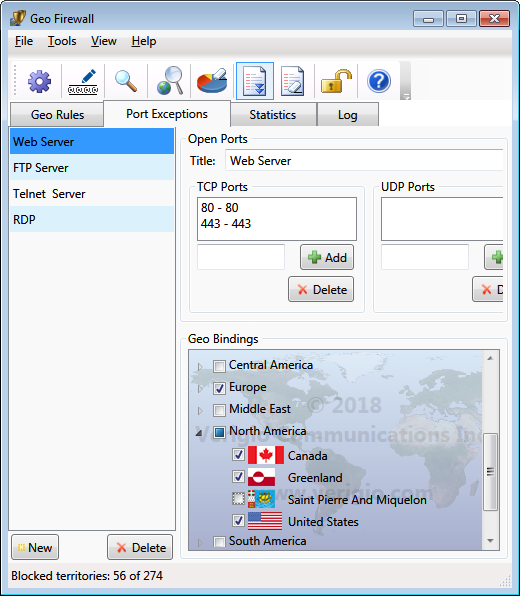
Check marks on countries in Geo Bindings denote the presence of the binding (association).
The Geo Bindings are persistent and do not change when associated countries change between blocked and allowed.
However, they have effect only on countries that are blocked (countries that are allowed allow all traffic anyway).
Reserved IPv4/IPv6 Networks
In addition to geographical territories, Geo Firewall also understands and works with reserved networks. These are the networks
used by computers to communicate with other computers and routers on local networks.
Reserved networks can be found under [Reserved Networks IPv4] and
[Reserved Networks IPv6].
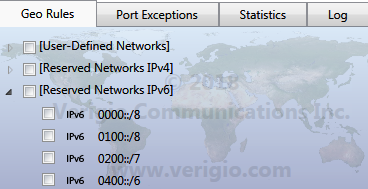
Reserved networks are pre-defined, and although they can be blocked or allowed, their definitions cannot be edited.
It is highly recommended not to block them to avoid unusual networking situations.
Some may ask:
what happens if [Reserved Networks] are
blocked? Nothing dangerous, really. The computer just
would not be able to reach other computers around it to obtain a new IP
address or to resolve domain names.
User-Defined Networks
In addition to pre-defined geographical territories and reserved IPv4/IPv6 networks, Geo Firewall allows to add user-defined
networks.
User-defined networks show up under [User-Defined Networks]
region.
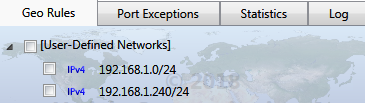
To edit user-defined networks, click
 on the toolbar.
Since IPv4 and IPv6 networks have different formats of IP addresses, they are kept separately during editing.
on the toolbar.
Since IPv4 and IPv6 networks have different formats of IP addresses, they are kept separately during editing.
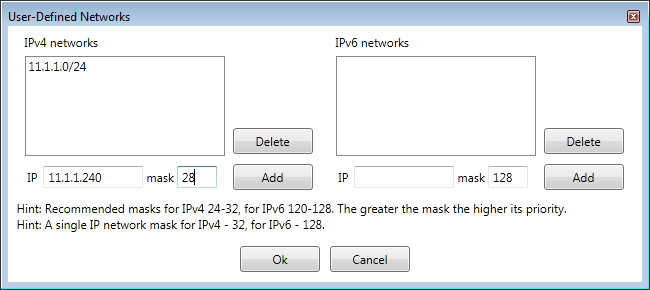
When editing user-defined networks, the networks can overlap with other user-defined networks or with pre-defined geographical
territories.
In such cases, there is an order of precedence for determining which rules are actually in effect for an IP address.
The more specific
networks (those that have greater network mask) always take precedence over less specific networks.
For example, the network 192.168.1.1/32 is more specific than 192.168.0.0/16, hence the rules for 192.168.1.1/32 will take
precedence during communication with 192.168.1.1.
A common way to unblock any specific network within already
blocked country is to create a user-defined network which is not
blocked (unchecked) or to add it to a white list of networks.
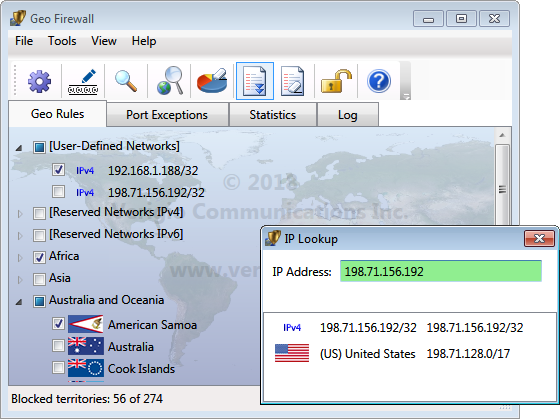
IP Geo Lookup
 is a great way to determine which network rules take precedence.
The more specific networks (those that take precedence) are listed at the top.
is a great way to determine which network rules take precedence.
The more specific networks (those that take precedence) are listed at the top.
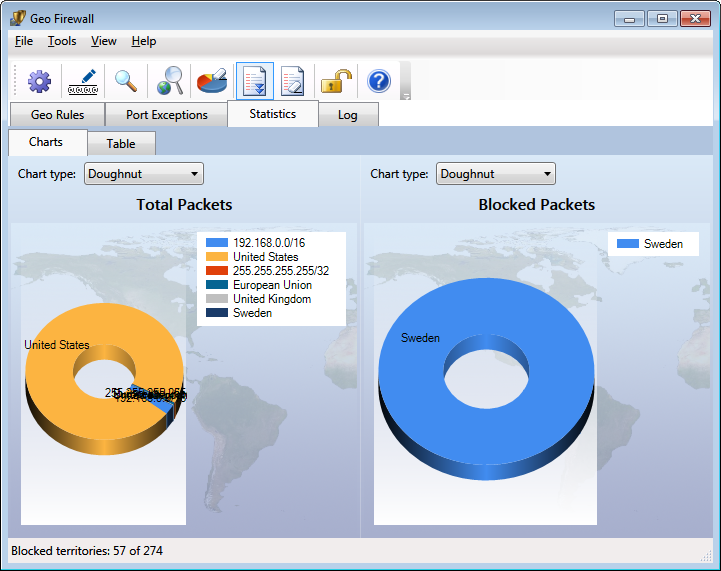
Statistics
Statistics makes it easy to understand where the traffic is
going to or coming from. Live statistics is presented in as a chart and
a table.
Statistical data is acquired/refreshed according to statistical refresh interval within Settings. The data
is also retired (removed) according to Remove Inactive Items settings.
The settings for statistics can be adjusted to include or exclude non-country records.
The collection and visualization of statistical data impacts CPU performance. On laptops and desktops there may be no significant
difference.
However on servers with weak graphics cards that operate at high CPU utilization, disabling of statistics or even
increasing of the refresh interval does significantly improve the overall system performance.
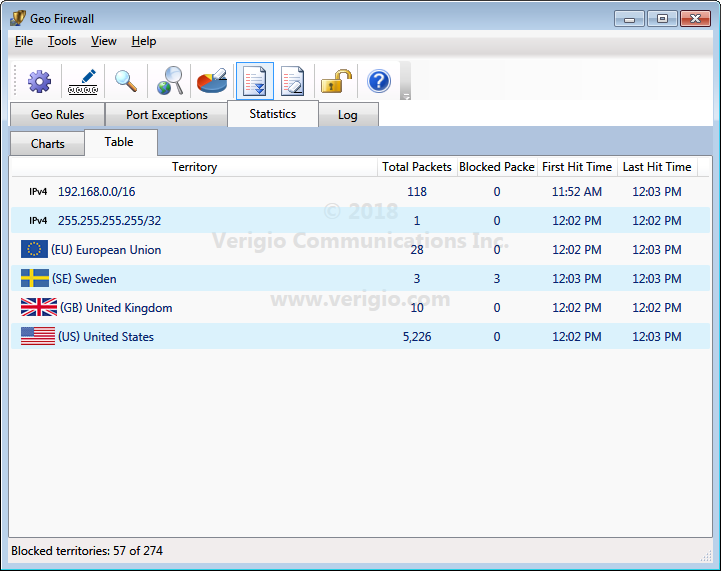
The data from the live statistical chart can also be viewed as a table.
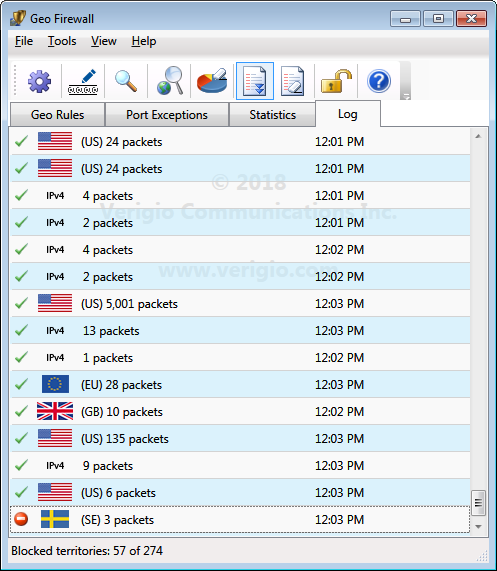
Log
Logging helps to see the historical performance of rules. Logging can be directed into
the log file (in CSV format) with a daily log file rotation.
The refresh rate of the visual log can be adjusted via Settings.
Just like with statistics, logging has an impact on CPU performance.
So, disabling or even increasing a refresh period may significantly improve the overall system performance.
Settings
Geo Firewall settings can be changed via Settings
 .
.
Geo Rules settings
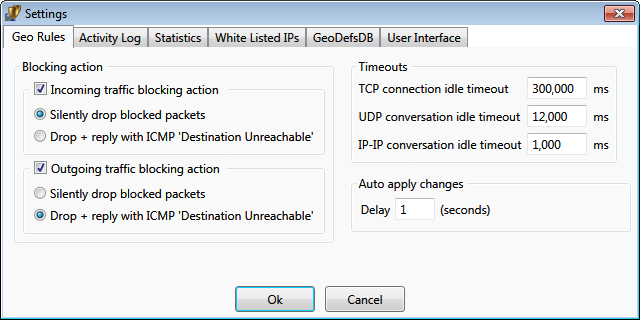
Blocking Action allows to specify the action to be performed on
the traffic that is being blocked. It is applied to all blocked territories and networks. If the action is unchecked,
blocking would not happen for that particular traffic direction.
-
Silently drop blocked packets - it forces to simply discard packets intended to/from blocked territories
-
Drop + reply with ICMP 'Destination Unreachable' - it forces to discard packets,
and also to reply to senders with the indication that the destination is unreachable.
This action is performed for every blocked packet.
This setting is recommended only for outgoing traffic to help local programs to faster realize that the destination
is inaccessible.
The well known "ping" utility shows the difference from the silent packet drop
mode.
Geo Firewall is filtering connections and conversations over the network. The traffic can be allowed in one direction, but
prohibited in the opposite direction.
Whenever the traffic starts in the allowed direction, Geo Firewall automatically allows traffic in directly opposite
direction only
to that specific communication point.
Timeouts specify how long the opposite direction for the connection point is open.
Example: Outgoing traffic to 'Fiji' is allowed, but the incoming traffic is blocked. In such case,
a computer with Geo Firewall connecting to a website (via TCP) on 'Fiji' would be able to receive
replies from 'Fiji' website until no packets are exchanged (the silence) for "TCP connection idle timeout" milliseconds.
Example: Outgoing traffic to 'Fiji' is allowed, but the incoming traffic is blocked. In such case,
a computer with Geo Firewall issuing a 'ping' to a server on 'Fiji' would be able to receive
a reply within 'IP-IP conversation idle timeout' milliseconds.
Activity Log settings
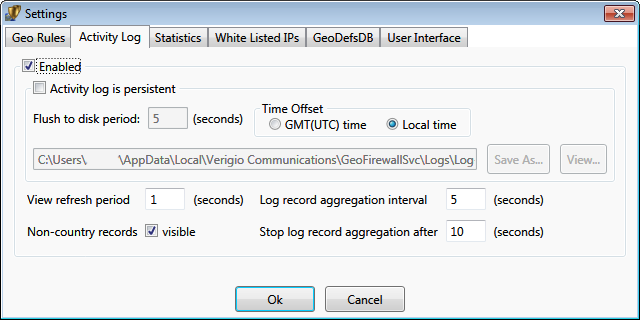
The activity log can be enabled or disabled. The disabling of activity log significantly improves overall system performance
due to reduction in graphics redraws.
The log can be persistent (stored to a hard drive) as a text file in
CSV format. A log file contains records for a single day (until the midnight). Log files are automatically
appended with the date of their creation. By default (when enabled), the persistent log files are stored into a system location
accessible only by computer administrators. The location is recommended to be changed.
The time zone for the events stored within the persistent log file can be GMT or based on the local time of the
system where the Geo Firewall user interface runs.
-
When multiple events (allowing or blocking) happening for the same territory, they are aggregated and reported as a number
of events of a certain type for the territory.
Log record aggregation interval specifies the interval for consecutive records to be aggregated.
So, the aggregation will be ongoing until the time between the records
exceeds the specified interval.
It also prevents flushing those records to disk while aggregation is ongoing.
Example: If aggregation interval is set at 5 sec, all records arriving within 5 seconds of each other will be aggregated
and displayed at once.
-
Since events could keep happening within the aggregation interval from each other for a very long time, it may prevent the
log records from being flushed to disk for a long time as well.
Stop log aggregation after allows to stop aggregation for already aggregated records and start a new aggregation
for future records. It specifies the maximum duration for each aggregation from its beginning.
Statistics settings
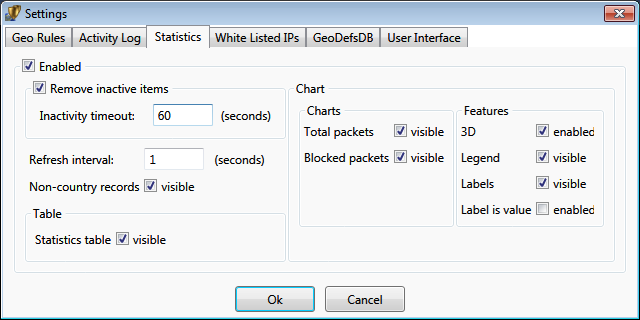
Statistical data could be accumulated for a long time. It is aggregated in a way similar to log events.
Inactivity timeout allows to remove from live statistics the events that happened some time in the past and
did not recently happened for the
specified timeout time.
White list settings
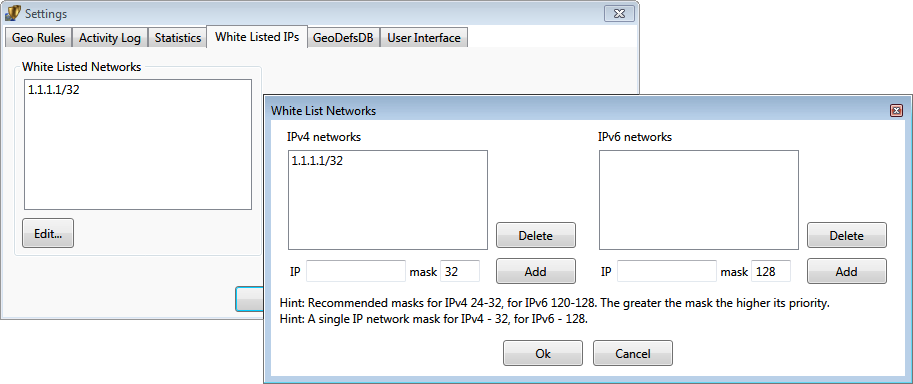
The whitelist of networks allows to specify the networks that will never be blocked. It usually contains IP addresses of local
computers or administrative servers.
The whitelist can have DNS names. The following 2 formats of DNS names are supported:
- Simple - the server name only. Example: verigio.com .
- Pattern - the server name with sub-domains. Example: *.verigio.com .
All DNS names are automatically resolved into IP addresses, then, those IP addresses are used for network traffic filtering. The simple DNS names are resolved into IP addresses on periodic basis specified within the settings.
The patterns can only have a single asterisk for sub-domains at the beginning. They are resolved into IP addresses by monitoring unsecure (UDP-based) DNS traffic.
Geo Definitions Database (GeoDefsDB) update settings
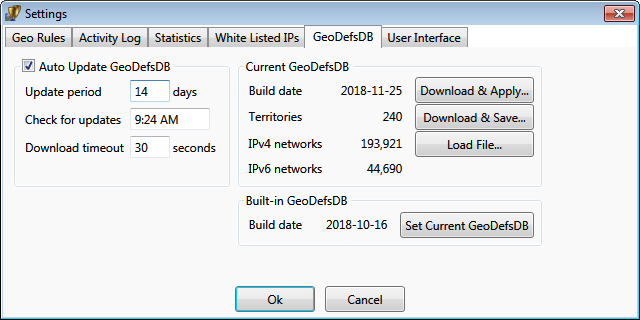
Geo definitions (Geo IP) database contains mappings between geographical territories and IP addresses.
This database is in proprietary format.
The program comes within the internal (embedded) Geo IP database that is used right after install. Updates to the
Geo IP database can be downloaded from our website using this settings page.
Depending on the product edition, the database can be set to update automatically at predefined time.
The initial time is generated randomly upon the first program startup.
The downloaded Geo IP databases are stored locally and can be applied manually when auto update is not enabled.
User Interface settings
Notes:
* Windows® is a registered trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.