Virtual Network Hub
Technical Specifications
| Latest release |
3.36 ,
22 Mar 2022 ,
[Change Log, Previous Releases]
|
|
Supported networking
|
Ethernet, IPv4, IPv6, TCP, UDP. |
|
Traffic transformation engine
|
Kernel-mode network driver. |
| Prerequisites |
.NET 4.5.2, up-to-date root certificates (or it will take
2 minutes to start).
|
| Supported OSes |
Windows 7*, 8, 8.1, 10, 11, Server 2008 R2*, Server 2012, Server 2012 R2, Server 2016, Server 2019, Server 2022.
*For Windows 2008 R2 and 7, required Service Pack 1 +
KB3033929 (SHA-2 digital signing).
*For Windows 8.1, Server 2012 R2, required KB2995730.
|
| Recommended hardware |
CPU 1GHz and above, modern graphics card. |
| Additional hardware required |
none |
Overview
Virtual Network Hub is an easy way to connect computers and devices into a single or several networks.
It has a visual appearance of a hardware network hub and creates a familiar environment for users
to apply their hardware settings onto this virtual device. The Drag-n-Drop interface allows to
visually assemble a hub and fine tune its settings for various networking tasks.
Virtual Network Hub brings a number of now popular features:
- WiFi HotSpot establishes a wireless network for other devices to connect to;
- Client for WiFi networks connects to other wireless networks;
- Wired networking supports direct/wired plugging-in to network cards;
- Internal DHCP server provides dynamic IP addresses for connecting devices;
- Internal DHCP client requests dynamic IP addresses and configuration from other routers;
Typical configurations:
Virtual Network Hub
IMPORTANT: When used on a Virtual Machine, accidental changes by a user to the rules may affect Remote Desktop (RDP) traffic and result in a user lock out.
For instructions on how to restore RDP connectivity for a VM, see KB article Restoring Remote Desktop (RDP) connectivity to Azure VM after a user lock out.
Virtual Network Hub has two main software components: the service and the user interface (UI).
The service can work without the UI. It performs monitoring and automatic reconfiguration of the underlying network
driver.
The UI manages configuration of the service and requires the service to be running.
UI shows available adapters on the left side and configurable networking hubs on the right side.
Each hub represents an isolated network segment. There are could be more than one hub
added to the hub list. The order of hubs can be changed
by dragging them or by clicking the hub ordering toolbar buttons

 .
The order of slots within a hub can also be changed by dragging them. However, the order does not make any difference
from the network routing perspective.
.
The order of slots within a hub can also be changed by dragging them. However, the order does not make any difference
from the network routing perspective.
Create a hub
To construct a hub, either select the existing hub with empty slot or create a new hub with
 .
Then, drag a network adapter from the left list onto an empty hub slot or a space behind the last assigned slot.
This would assign the adapter to the existing slot or create a new slot and assign the adapter to that new slot.
Alternatively, a network adapter can be assigned to a new slot of the selected hub by clicking
.
Then, drag a network adapter from the left list onto an empty hub slot or a space behind the last assigned slot.
This would assign the adapter to the existing slot or create a new slot and assign the adapter to that new slot.
Alternatively, a network adapter can be assigned to a new slot of the selected hub by clicking
 button of the network adapter.
button of the network adapter.
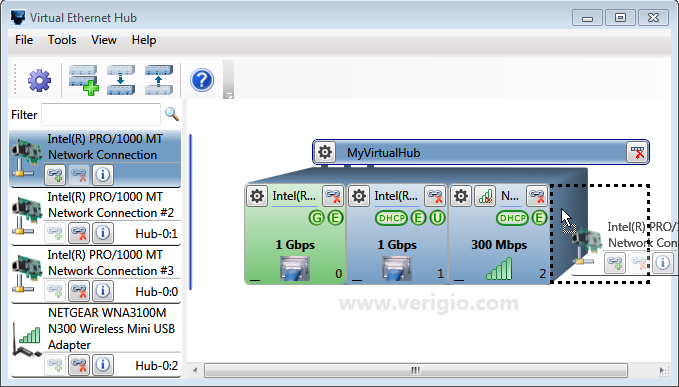
All changes to hubs are applied automatically with a short delay as configured within UI settings
 .
.
A network adapter can be assigned only to a single hub slot. Each slot has its own configurable settings
 that define functionality of the slot.
that define functionality of the slot.
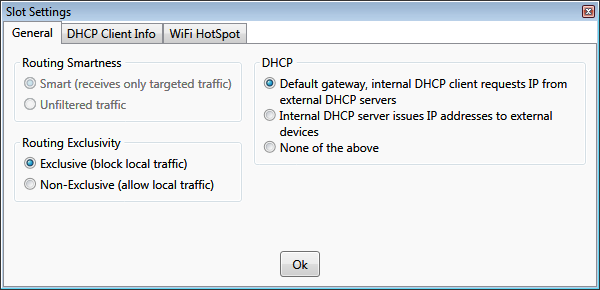
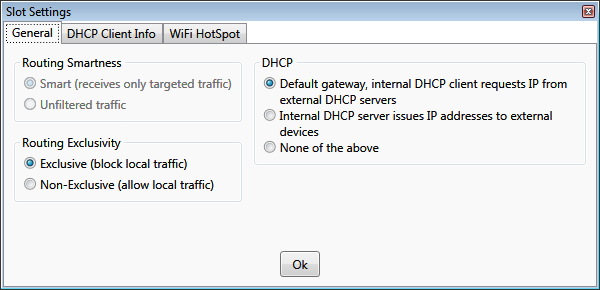
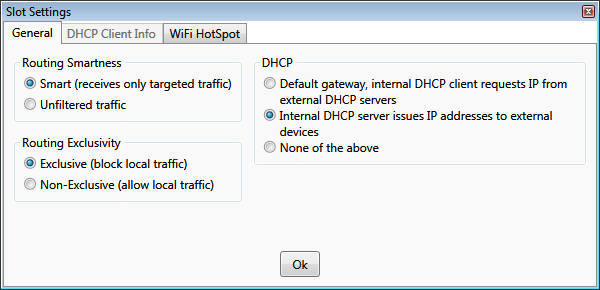
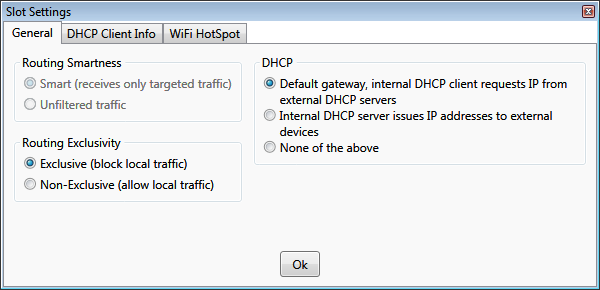
Hub slot settings

DHCP
Routing Smartness
-
Smart - the slot receives only the traffic intended for the device connected to it. All other traffic that is passing
between other slots of the hub is filtered out.
-
Unfiltered
 -
the slot receives all traffic without filtering. The traffic passing between other hub slots is visible to the device connected
to this slot.
This setting is often used for network monitoring and it turns the slot into a slot of a network switch.
-
the slot receives all traffic without filtering. The traffic passing between other hub slots is visible to the device connected
to this slot.
This setting is often used for network monitoring and it turns the slot into a slot of a network switch.
Routing Exclusivity
Network adapters on the computer running Virtual Network Hub can be used not only by Virtual Network Hub itself, but also
by other programs.
-
Exclusive
 - the network adapter associated with the slot is used exclusively by the Virtual Network Hub. Other programs
do have access to the network adapter, but all their traffic passing through the associated network adapter is silently
discarded.
- the network adapter associated with the slot is used exclusively by the Virtual Network Hub. Other programs
do have access to the network adapter, but all their traffic passing through the associated network adapter is silently
discarded.
-
Non-exclusive - the network adapter associated with the slot can be used by all programs on the computer. All traffic
from other programs passing though this slot is routed according to the hub settings.
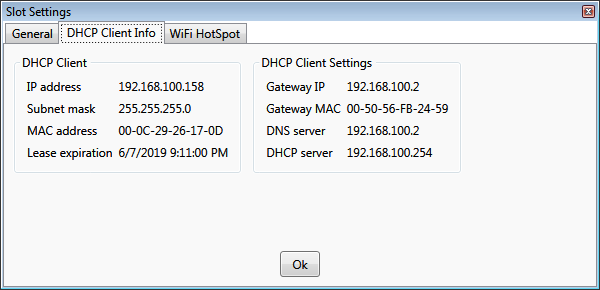
DHCP client info
When a slot is designated as a default gateway, it acquires its IP address dynamically from the uplink router. The acquired
IP can be viewed on the
DHCP Client information tab.
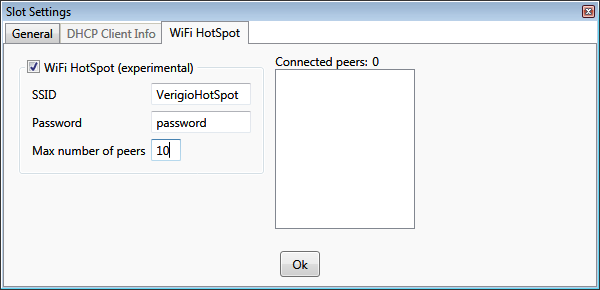
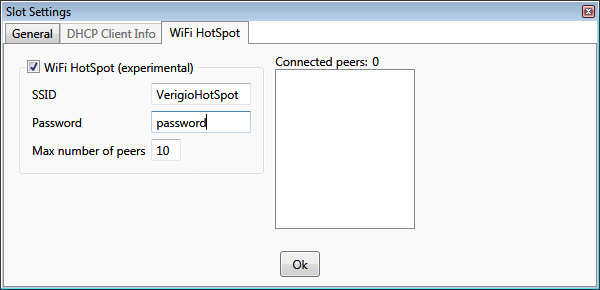
WiFi HotSpot
A hub slot with an assigned wireless network adapter can act as a WiFi HotSpot. Only a single HotSpot is supported amongst
all running hubs.
Not every wireless network card supports WiFi HotSpot functionality. Only the network cards with SoftAP mode
explicitly stated in their specification support that.
|
To enable WiFi HotSpot functionality check the appropriate box and provide the settings for the HotSpot. The WiFi HotSpot
slot is highlighted with a golden color.
All additional parameters including DHCP server and slot exclusivity are
set automatically.
The 'Connected peers' list is automatically refreshed to show MAC
addresses of the connected wireless devices. The device is considered to be connected after it provides the correct password and
is fully ready to communicate.
|
|
Hub settings

Hub settings include configuration shared by all hub slots.
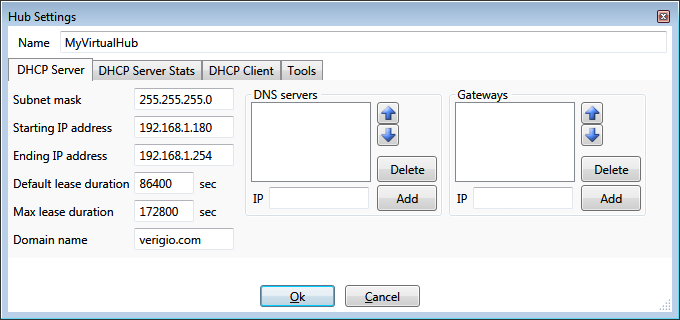
DHCP Server
Each hub has a single DHCP server instance.
Hub's DHCP server provides IP addresses
for all hub slots that are configured within their settings to provide dynamic IP addreses by internal DHCP server.
-
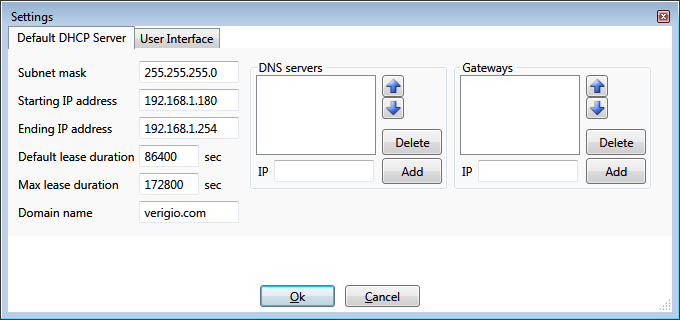
Subnet mask - allows hub to determine which IP addresses are outside of the current sub-network and when to route
packets onto default gateway slot.
-
Starting and Ending IP addresses - they define the range of dynamic IP addresses issued to clients. This range should
have at least 2(two) IP addresses. The highest IP address is taken by DHCP server itself and is not issued to connected
devices.
-
Default lease duration - the default value is 24hr. The leases of this duration are issued when connected clients
do not request any specific lease duration. The leases are periodically extended by connected devices upon their requests.
This value should not be too large to avoid running out of IP address space when disconnecting devices do not explicitly
release their IPs.
-
Max lease duration - it is the maximum lease duration issued by DHCP server when a DHCP client requests too long
lease duration.
-
Domain name - it is a unique domain name will be provided to DHCP clients. It is a textual name which the clients
would use for resolving their own name and names of neighboring devices when no other information is available.
-
DNS servers - additional DNS servers to be provided to DHCP client. When a hub has a default gateway, the DNS servers
from the default gateway are automatically provided to DHCP clients as the top DNS servers. Whenever a hub does not have
a default gateway, the DNS servers from the settings list are the only DNS servers provided to DHCP clients.
-
Gateways - default gateways to be provided to DHCP clients. Whenever a hub has a default gateway slot, its IP is
automatically provided to all DHCP clients as a top default gateway. However, when a hub does not have a default gateway
slot, the Gateways from the settings list are the only gateways provided to DHCP clients.
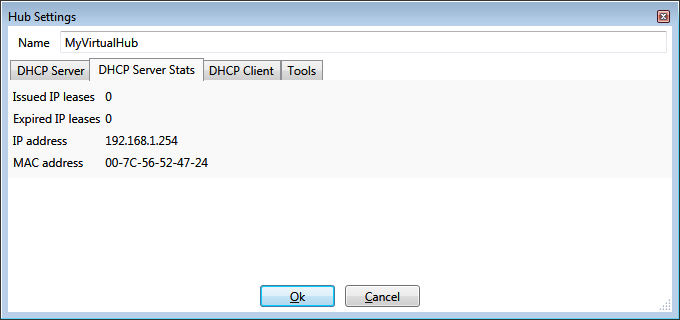
DHCP Server Stats
DHCP server statistics can be seen on the DHCP Server Stats tab.
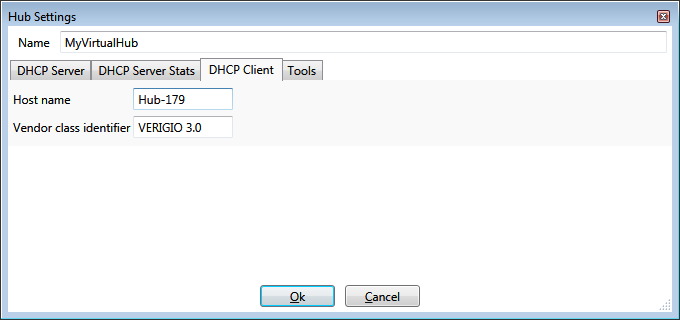
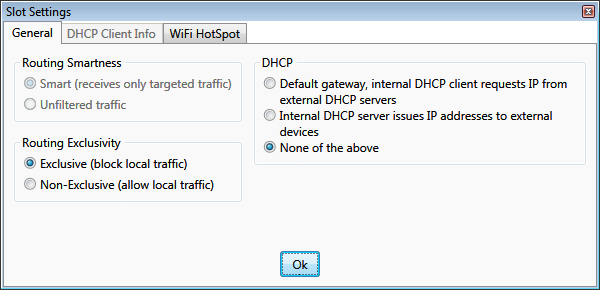
DHCP Client
A hub slot can be designated as a default gateway. Such default gateway functionality includes a DHCP Client that obtains
IP address dynamically from the uplink router.
DHCP Client settings define the identification the default gateway slot (DHCP Client) will provide to the uplink
router (or another DHCP server) to obtain the IP address.
Program-wide settings

Besides settings for hubs and for slots, Virtual Network Hub has program-wide settings.
Default DHCP Server
'Default DHCP Server' settings simplify configuration of DHCP servers for new hubs. These settings are copied into
new hubs upon their creation.
User Interface
Various user interface settings can be adjusted to user preferences.
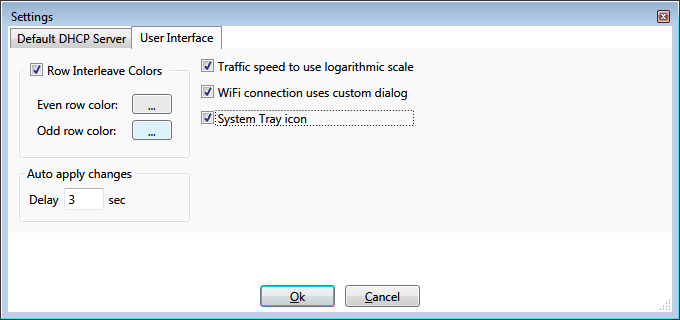
The user interface can be configured to minimize to the system tray area when attempted to close.

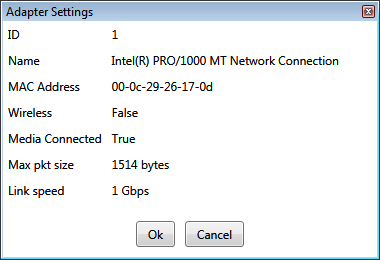
Network Adapter info
The status of each network adapter can be retrieved by clicking
 icon on the network adapter.
icon on the network adapter.
Typical configuration examples
WiFi HotSpot with a gateway into a wired network
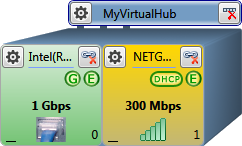
-
Slot-0 (wired connection, gateway)
-
Slot-1 (wireless connection, WiFi HotSpot)
Wired network router
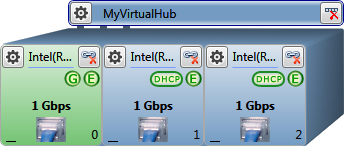
-
Slot-0 (wired connection, gateway)

-
Slot-1 and Slot-2 (wired connection)
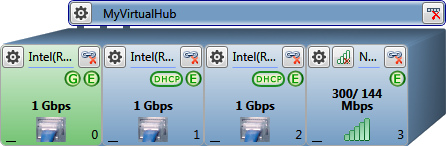
Wired network router with dial-out wireless connection
-
Slot-0 (wired connection, gateway)

-
Slot-1 and Slot-2 (wired connection)

-
Slot-3
(wireless connection, dial out)
Wired network router with wireless gateway
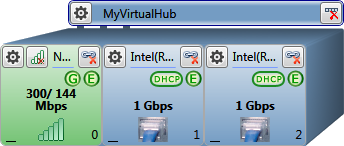
-
Slot-0 (wireless connection, gateway)
-
Slot-1 and Slot-2 (wired connection)

Notes:
* Windows® is a registered
trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.